AI: Foundations and Value in Heterogeneous VMs Environments
AI agents transform how teams run compute workflows, and they do so by combining autonomy, context, and action. First, an AI agent monitors inputs, then it reasons over signals, and finally it executes tasks. Also, these agents reduce manual steps and improve speed. For example, large language models and language models power natural language interfaces that let operators query video and logs. The visionplatform.ai product suite shows this pattern: it turns cameras and VMS data into searchable knowledge, and then it allows agents to recommend actions and pre-fill incident reports. Furthermore, in many control rooms raw detections overwhelm staff; so AI brings context, and thus it reduces false alarms and time per alarm. Also, researchers highlight the need for “secure execution” and “rapid fail-back” across diverse platforms here. This research reports up to a 40% reduction in downtime from improved fail-back strategies here. Therefore, AI provides clear operational value when it can run reliably across different hardware and OS combinations.
Next, LLMs and llms enable agentic behavior by sequencing subtasks, by calling external APIs, and by summarizing long timelines. Also, the integration of video descriptions into agent reasoning is a practical example: an on-prem Vision Language Model in our stack converts raw video into textual events that an agent can reason about, and that supports controlled environment policies. In addition, AI helps orchestrate workflows across cloud servers, servers on-prem, and edge devices. As a result, teams can automate rule-based tasks, and they can scale monitoring without exposing sensitive data. Finally, using an ai platform that exposes VMS events as structured inputs makes it easier to connect decision logic to operational systems. Consequently, agents can leverage context, act with auditable steps, and maintain compliance.
Heterogeneous: Addressing Diversity in VM Types and Platforms
Heterogeneous infrastructures mix virtual machine images, hardware accelerators, and operating systems. First, sources of heterogeneity include OS variations, different accelerator types such as GPU or TPU, container images, and the split between cloud providers and on-prem servers. Also, edge devices and NVidia Jetson boards introduce more diversity when work moves across devices. Next, this variety challenges interoperability because agents must run across different runtime ABI, file systems, and networking stacks. For that reason, teams need abstractions that present a consistent API for orchestration, and they need environment discovery tools that detect capabilities and installed libraries. For example, a discovery agent can list whether a virtual machine has GPU accelerator support, what container runtime it uses, and which network policies apply. By detecting these traits, the system can adapt workload placement and ensure safe execution.
Then, configuration consistency matters. Use immutable container images when possible, and use configuration-as-code to maintain identical behavior across kubernetes clusters and serverless endpoints. Also, containerization reduces variability and speeds deployment. However, some sites prefer strictly on-prem models to protect sensitive data. In those cases, a hybrid approach helps: run vision models and the Vision Language Model in a controlled environment on-prem, and then orchestrate higher-level agents that only carry metadata. In addition, integration of heterogeneous systems requires mapping VMS events to a common schema, and this mapping supports downstream indexing for forensic search forensic search. Finally, use lightweight agents to report resource utilization, to surface the ability to integrate new drivers, and to help plan fail-back when a vm can host multiple services.

AI vision within minutes?
With our no-code platform you can just focus on your data, we’ll do the rest
AI Agent: Design and Orchestration for Distributed Compute
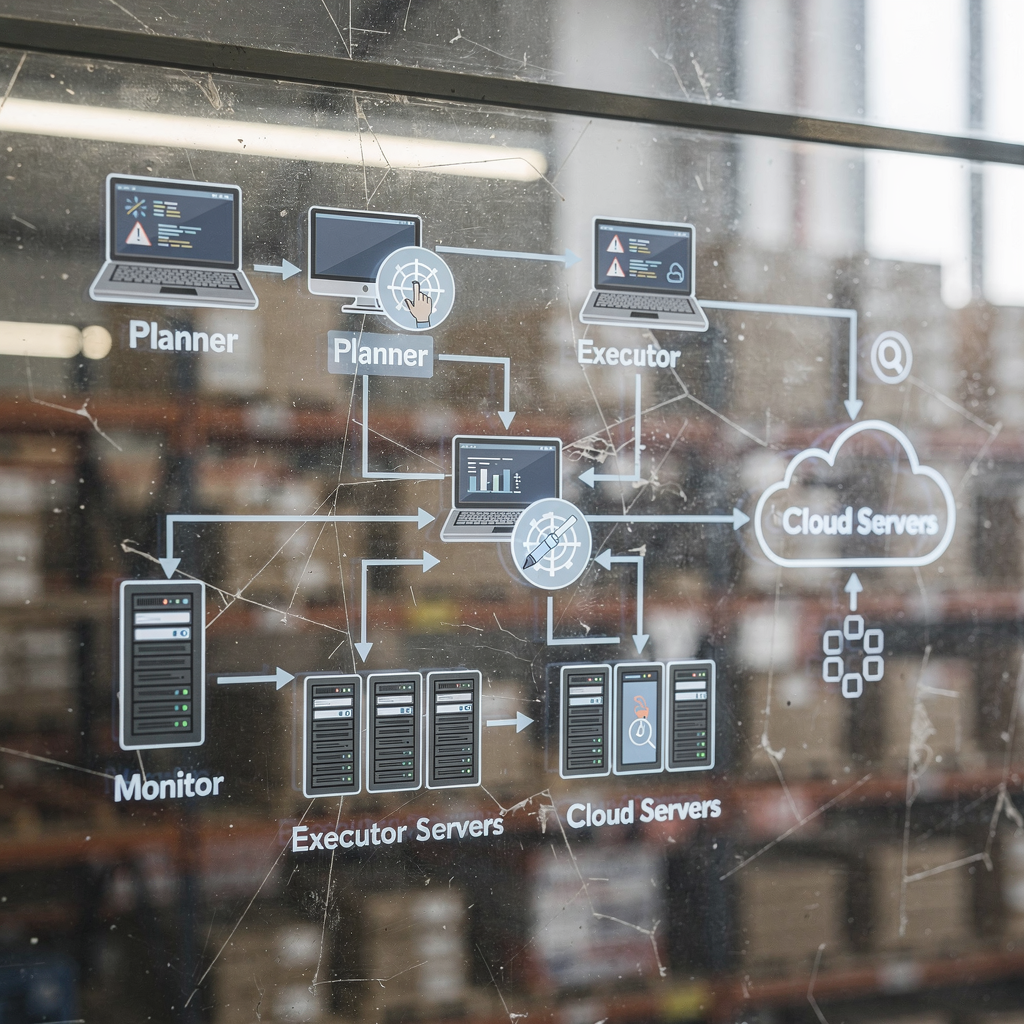
Designing an ai agent for distributed environments begins with clear modular components: planner, executor, and monitor. The planner ingests objectives, formulates steps, and selects the right compute targets. Then, the executor runs tasks on chosen nodes, and it uses secure channels for data source access. Meanwhile, the monitor tracks health, latency, and resource utilization so the planner can re-schedule when needed. Also, for larger efforts consider multi-agent coordination. Multi-agent coordination uses lightweight messaging and event buses to let agents share intents and to avoid duplicated work. For instance, a coordinator might assign a data-ingestion job to an edge agent and an inference job to a high-performance server. In multi-agent systems, design for eventual consistency and for safe state transfer across agents within the same operation.
Next, communication protocols must be resilient. Choose encrypted channels, heartbeat checks, and simple state reconciliation rules. Also, add policy guards that block actions outside approved scopes. For fail-over, implement rapid fail-back and adaptive scheduling algorithms that detect node degradation and then migrate tasks to warm standby targets. Research shows that frameworks built for heterogeneous environments can cut downtime by about 40% with improved fail-back strategies source. Moreover, coordinate recovery with orchestration systems like Kubernetes and with serverless fallbacks when appropriate. Also, consider using a small ai platform or a control plane that exposes an API for agents to query available resources, such as whether a node supports a required accelerator or contains a local database. Finally, design agents to handle raw data, to preprocess unstructured data, and to call downstream machine learning models for inference or retraining. This keeps the system adaptive, and it improves the overall adaptability to dynamic load patterns.
VMs: Secure Deployment and Resource Management Workflows
Deploying agents to virtual machines requires repeatable installation and strict controls. First, build container images or use configuration scripts that contain only necessary binaries. Also, prefer immutable images that reduce drift across deployments. For on-prem security, ensure that video and models remain inside the site to stay aligned with EU policy and with customer requirements. In practice, visionplatform.ai operates with fully on-prem processing by default so video never leaves the facility. Next, secure execution means encrypting data in transit and at rest, and using access control to limit which agents can call sensitive APIs. Also, sign container images and verify signatures at runtime to prevent tampered deployments. For communication use mutual TLS or equivalent, and rotate keys regularly. Additionally, limit privileged access and run agents with least privilege.
Then, control resource consumption with quotas and autoscaling policies. Monitor resource utilization with lightweight exporters, and hook alerts to a central dashboard for real-time visibility. Also, enforce quotas on CPU, memory, and accelerator time so a single resource-intensive job cannot starve the rest. For cost and performance, track a metric such as cost per task and average latency per inference. Use these metrics to iterate on placement rules and scheduling heuristics. In some deployments, defining a serverless fallback works: when a high-performance host fails, route lightweight tasks to a serverless endpoint or to a different server. For sensitive data, design workflows that avoid moving raw video offsite. Instead, expose metadata and converted descriptions as the data source that agents can query. Finally, use cryptographic isolation and audit logs to ensure actions are traceable, and to support compliance audits.
AI vision within minutes?
With our no-code platform you can just focus on your data, we’ll do the rest
Use Case: End-to-End Multi-Agent Workflow Examples
Here are three concise use case examples that show agents across heterogeneous infrastructure. First, a data-ingestion pipeline spans edge, cloud environments, and on-prem VMs. Edge agents extract frames, then a Vision Language Model on a local server converts images to text. Next, a central indexer stores the descriptions into a searchable database, and an ai agent handles alerts. Also, this sequence supports forensic search and natural language queries so operators can find incidents quickly forensic search. For heavy workloads, raw frames can be sampled, and unstructured data can be summarized before transmission. Then, fail-back occurs if an edge node goes offline: the planner reassigns ingestion to a nearby vm, and the system keeps processing with minimal delay. This design supports end-to-end traceability, and it remains compliant in a controlled environment.
Second, a distributed inference use case uses multiple agents to balance latency and cost. An initial lightweight model runs on Jetson edge devices to filter events, and more complex inference runs on a cloud-native server or on an on-prem high-performance server with GPU accelerator. Also, agents coordinate to route frames to the right accelerator. Using a common orchestration layer and container images simplifies deployment, and using kubernetes clusters for heavy workloads allows automatic scaling. Third, an error-recovery flow shows how agents hand off tasks across different environments. When a detection stream loses connection, a monitoring agent triggers retries, then it notifies a human-in-the-loop agent if retries fail. Also, a reasoning agent can verify alarms and either close false positives or escalate with recommended actions. In practice, the VP Agent Reasoning feature correlates multiple inputs, and then it suggests operational steps that match procedures, which reduces operator load. Finally, these patterns highlight the need for the ability to integrate VMS events with external systems like access control or incident tracking, and they show how to automate routine tasks while preserving oversight.
Metric: Key Performance Indicators for Reliability and Efficiency
Choosing the right metric helps you measure reliability and efficiency. First, define throughput (tasks per second), latency (ms per inference), and fail-back time (seconds to restart work on alternate nodes). Also, include cost per task to capture economic efficiency. For video-centric systems, track end-to-end time from detection to action, and track how often agents close incidents automatically. Additionally, monitor resource utilization and accelerator occupancy to optimize placement. Research shows a 25% reduction in computational overhead from adaptive resource management, and a 30% increase in confidentiality compliance with secure execution protocols source. Use such benchmarks to set targets.
Next, adopt continuous monitoring with alert thresholds and dashboards. Tools that collect metrics across kubernetes distribution, serverless functions, and bare-metal servers let you see end-to-end trends. Also, add synthetic tests that exercise fail-back paths regularly so recovery time objectives stay valid. For interpretation, compare metrics before and after changes to agent logic or to container images. Then, iterate: for example, reduce latency by moving a heavy model to a more proximate high-performance server, or reduce cost by batching inferences. Additionally, use A/B experiments to test scheduling heuristics and to validate improvements. Finally, tie metrics back to operational goals. If the control room aims to cut false alarms, monitor the percentage reduction and the time saved per alarm. As a result, you can align technical work with operational KPIs and you can prove ROI for the effort.
FAQ
What is an AI agent in a heterogeneous VM environment?
An AI agent is an autonomous software component that observes inputs, reasons about them, and acts across different infrastructure. It runs tasks on diverse nodes, coordinates with other agents, and adapts to changing resources.
How do I ensure secure execution of agents on VMs?
Encrypt traffic, sign container images, and enforce least-privilege access controls. Also, keep sensitive video and models in a controlled environment and audit all agent actions for traceability.
How do agents handle fail-back across different environments?
Agents implement health checks and heartbeat messages, then they trigger adaptive scheduling when a node degrades. Rapid fail-back migrates work to standby hosts with minimal interruption, and synthetic tests validate the path.
Can I run inference on edge devices and on cloud servers together?
Yes. Use lightweight models at the edge to filter data, then run heavier models on high-performance servers or cloud servers when needed. Orchestration decides placement based on latency and cost.
What metrics should I track to measure reliability?
Track throughput, latency, fail-back time, and cost per task. Also, monitor resource utilization and the percentage of incidents resolved automatically to align with operational objectives.
How does visionplatform.ai support on-prem privacy requirements?
visionplatform.ai keeps video and reasoning on-prem by default, and it exposes structured VMS events to agents without sending raw video offsite. This helps meet EU AI Act and other compliance needs.
What role do LLMs play in agent workflows?
Large language and language models allow agents to interpret natural language queries, summarize timelines, and craft human-friendly explanations. They make search and reasoning accessible to operators.
How do I maintain consistent configuration across many VM images?
Use immutable container images or configuration-as-code, and deploy through orchestrators like kubernetes clusters. Also, include environment discovery to detect installed accelerators and runtime differences.
What is the best way to integrate VMS events into automation?
Map VMS events to a common schema and expose them as a structured data source that agents can query. For forensic workflows, use searchable descriptions so operators and agents can find incidents quickly forensic search.
How do I balance autonomy and human oversight?
Start with human-in-the-loop actions for medium-risk scenarios, then gradually move low-risk, repetitive tasks to autonomous flows with audit trails. Always maintain escalation rules and the ability to revert automated actions.

