intelligent search in Genetec Security Center
Intelligent search in security systems means the system understands context, not just timestamps. In Genetec Security Center this capability moves searches from simple metadata lookups to meaning-based queries. For example, an operator can type a natural language phrase like “person wearing a red jacket entering through the main door” and the system returns matching clips. This form of forensic search removes the need to know camera IDs or exact recording times. As a result, teams can perform a targeted quick search and get results in far fewer steps.
Semantic indexing builds rich descriptions of scenes. Consequently, algorithms tag objects, attributes and actions. The system labels people, vehicles and bags. Then it links those labels to events such as entry and exit or loitering. Because the index is contextual, investigators can target your video search by describing behaviour and appearance instead of hunting through metadata. For operators who want a concise user guide, the platform exposes search capabilities in an intuitive interface.
Dr. Marie Dupont captures the benefit well: “Semantic video search transforms video surveillance from a passive recording tool into an active intelligence asset. By enabling natural language queries, it democratizes access to video data and accelerates incident response times.” This quoted insight explains why investigation teams value semantic tools and why many security teams adopt them. For more on how forensic search works in transport environments see our article on forensic search in airports: forensic search in airports.
Finally, the new quick search tool helps focus results without lengthy setup. Because the search tool helps you target specific moments, users spend less time opening camera streams. In this way, intelligent search helps you uncover evidence faster while simplifying the basic search workflow.

speed up investigations with semantic video search
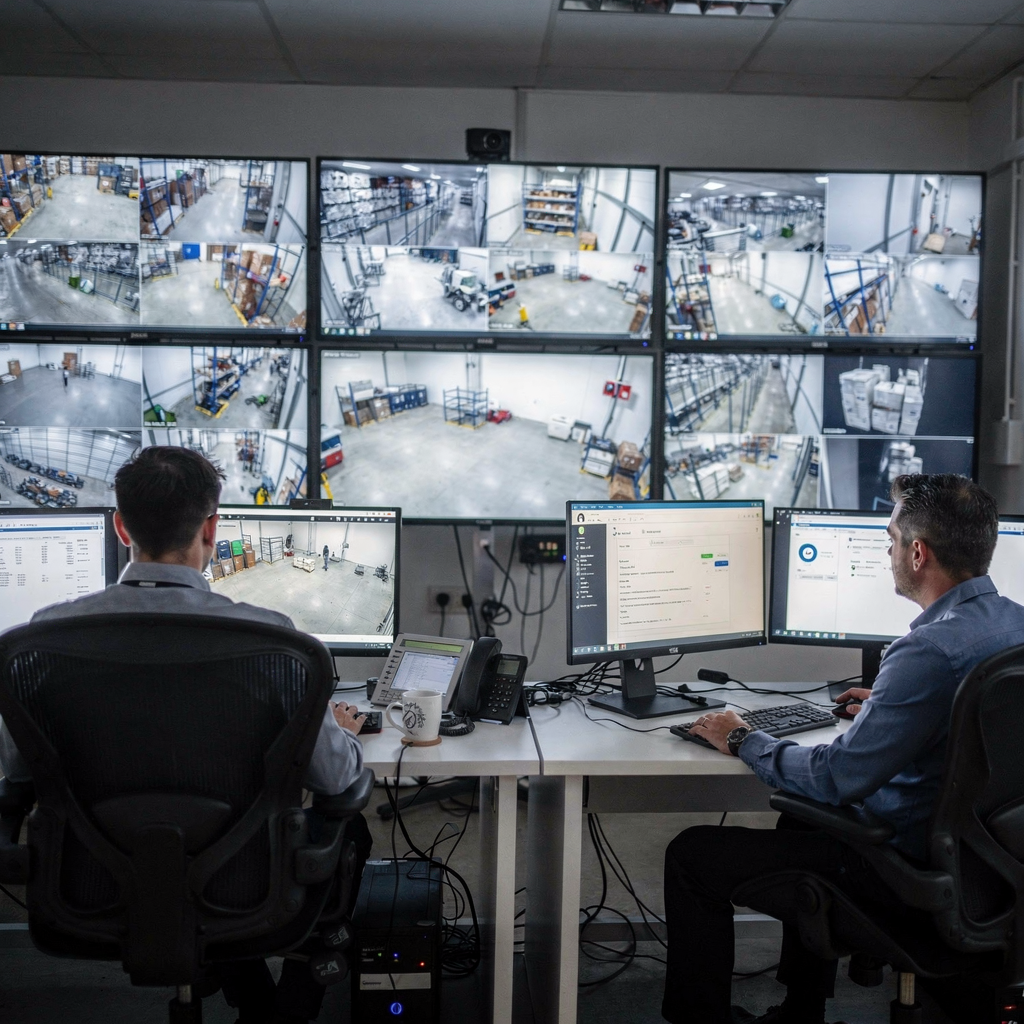
Semantic video search can speed up investigations by making the search itself faster and more reliable. In trials, organizations reported a 50% increase in the accuracy of video search results when using semantic search compared to traditional metadata-based methods, which means fewer false leads and more productive time per case (source). Additionally, product literature states that semantic video search can reduce the time required to locate relevant footage by up to 70% (statistic). These gains are measurable and repeatable.
Real-time indexing matters. Modern systems can index live streams so that a quick search of playback video returns near-instant results, even across very large archives. This capability allows investigators to run a quick search and then jump to the exact moment the event occurred. As a result, teams can close cases faster because they view only relevant clips. For large sites, federation and central indexing let teams search across multiple sites without manual aggregation. That approach supports complex multi-camera incidents and shortens the investigation experience.
Furthermore, analytics drive precision. Deep neural models analyze frames and metadata to surface scenes of interest. These models supply attribute tags such as clothing colour and vehicle type, which help investigators target their video search to get faster results. For incident response that needs to find people or objects of interest, this level of detail speeds identification and reduces manual review time. The combination of fast indexing and accurate classification is what helps you target your video in high-pressure investigations.
Finally, teams using a security center saas or on-prem instance benefit from near-real-time search. Whether a site uses a cloud service or a local video management system, semantic indexing reduces time to insight and helps investigation teams resolve cases sooner (deep learning reference).
AI vision within minutes?
With our no-code platform you can just focus on your data, we’ll do the rest
investigation use cases across sectors
Semantic search supports many types of investigation. In transportation, security teams use contextual queries to find suspicious behaviour or to locate lost items. For example, operators can search for “person leaving a bag at a gate” and then jump to the exact timeline across multiple cameras. Airports often combine license plate recognition with semantic tags to track vehicles in and out of zones. For more on automatic vehicle and plate workflows see our ANPR resource: ANPR/LPR in airports.
Retail teams also benefit. They use semantic indexing to study customer paths, generate heatmaps and optimise store layouts. When combined with people counting and occupancy analytics, these insights improve operations and customer flow. The platform can identify people and objects of interest and then correlate that information with entry and exit times to model checkout bottlenecks. For evidence-based layout changes, the system offers an intuitive functionality that simplifies analysis for non-technical staff.
Law enforcement uses semantic search for case work. Investigators can search for “red vehicle entering after midnight” and receive clips from across the site. That ability to search for evidence in plain terms lets officers find evidence without specialist tagging. For airports and transport hubs, semantic search pairs well with perimeter and intrusion detection to speed incident triage. For examples of perimeter and intrusion workflows see our intrusion detection page: intrusion detection in airports.
Across sectors the same themes repeat. Semantic search helps you target your video when time matters. It reduces manual review, supports federated searches across multiple sites and improves the chance of resolving cases quickly. Consequently, video investigations become less about data retrieval and more about actionable insight.
empower security teams with natural language queries
Natural language queries change who can run investigations. Previously, only trained analysts could tag footage and build complex queries. Now, a security operator can type a short description and find the clip. The new intelligent interface removes the need for specialist training. As a result, more staff can run basic investigations and glean situational context quickly.
Dr Marie Dupont highlighted this shift: “Semantic video search transforms video surveillance from a passive recording tool into an active intelligence asset.” That idea captures how search helps you uncover key details and why security teams value intuitive tools. Because the interface supports free-text queries, investigation teams do not need to learn complex metadata schemas or to read technical documentation before they begin.
Also, this approach can empower field teams. For instance, a guard at a remote gate can run a quick search to confirm an identity or to find the exact moment a vehicle passed. The technology links to access control logs and other systems so that a query returns a contextual answer, not just a clip. In this way, the solution is based on intelligent automation and yet remains governed by clear policies and audit trails.
Finally, the search reduces cognitive load during incidents. Operators receive prioritized results and recommended next steps, which help close cases faster. The system also supports a “performing a targeted quick search” mode for high-pressure situations, which presents the most likely clips first so teams can act without delay.
AI vision within minutes?
With our no-code platform you can just focus on your data, we’ll do the rest
unify video data and metadata in a single platform
A unified approach helps teams work faster. A unified security platform connects live streams, archived footage and alarm metadata in one interface. This design reduces the need to switch between systems and it helps you find evidence from a single dashboard. In practice, operators see alarms, maps and search results in one view so they can resolve cases without pulling multiple tools together.
Security center saas offerings and on-prem deployments both benefit from this unified model. Federation capabilities allow a central team to query distributed sites while keeping data local when required. That architecture supports multiple sites and complies with strict data policies. Many organisations prefer a hybrid approach that lets them unify operations while maintaining control over sensitive footage.
Integration with access control and intrusion detection systems multiplies value. For example, when an access control event occurs, the system can auto-populate a timeline and show the exact moment a badge was used. Likewise, license plate recognition tags can be overlaid on vehicle tracks to simplify follow-up. For details on license workflows, see our vehicle detection and classification resource: vehicle detection and classification in airports.
Finally, the platform supports open architecture. That design ensures technical documentation and APIs are available for system integrators and saas users. Because the architecture is open, teams can combine best-of-breed analytics and keep control of models and data. This approach helps organisations meet compliance requirements in the EU and beyond while still benefiting from advanced search capabilities.
automation of video indexing with AI
Automation matters because manual tagging cannot scale. Deep learning models automate the indexing process. Convolutional and recurrent neural networks process spatial and temporal data to label scenes. These models support object detection, attribute recognition and behavioural analysis. For a technical overview of relevant models see this survey of deep learning for forecasting and sequence tasks (reference).
Capabilities include detection of people and vehicles, recognition of clothing or vehicle type, and alerts for behaviours such as loitering or crowd formation. The system can identify people and objects and then flag people and objects of interest for review. Continuous model training improves performance on site-specific classes. Edge-and-cloud deployment options let teams choose where processing happens to meet policy and latency goals.
Automation also enhances the investigation experience. For example, investigators can search for a specific attribute and receive results ranked by relevance. The timeline and associated metadata highlight the exact moment an event occurred. That feature helps teams find people and other clues more quickly and it reduces time spent scrubbing hours of video. In practice, automation and applied analytics let teams perform video investigations with much greater speed and consistency.
Finally, because our company visionplatform.ai focuses on reasoning layers and on-prem vision language models, operators gain explanations alongside alarms. This combination of automated indexing and human-friendly descriptions helps teams make decisions that are repeatable and auditable. It also supports future capabilities such as agent-driven actions and controlled autonomy based on intelligent automation.
FAQ
What is semantic video search?
Semantic video search uses AI to index video by meaning rather than by tags or timestamps. It allows users to enter a plain-text description and retrieve relevant clips across cameras and time.
How does semantic search speed up investigations?
Semantic indexing reduces the time to find relevant footage by surfacing clips that match descriptions, not just file properties. In trials, organisations have reported both faster results and higher accuracy when compared to traditional searches (source).
Can non-technical staff run searches?
Yes. Natural language queries let guards and supervisors find clips without specialist training. The interface provides intuitive functionality and suggested queries to help new users.
Does semantic search work across multiple cameras?
Yes. Federation and central indexing let teams search across multiple cameras and sites at once. That capability supports multi-camera incidents and city-scale monitoring.
How accurate are the detections?
Accuracy varies by model and site, but pilot deployments have shown up to a 50% improvement in search result accuracy over metadata-based methods (study). Continuous training improves detection over time.
Can semantic search integrate with access control logs?
Yes. Integrations with access control and other systems create contextual timelines that show entry and exit events alongside video. This helps investigation teams correlate video and system events quickly.
Is the video processed in the cloud?
Deployment options include cloud, on-prem and hybrid. Many organisations prefer on-prem processing for compliance. visionplatform.ai supports on-prem Vision Language Models to keep video and models inside the environment.
What kinds of analytics are used?
Systems use object detection, attribute recognition and behavioural analytics. Convolutional and recurrent models extract spatial and temporal features to build rich metadata (research).
Can semantic search help find license plates?
Yes. License plate recognition can be combined with semantic tags to track vehicles and to search for plate numbers or vehicle types across timelines.
Where can I learn more about integrating semantic search?
Consult product technical documentation and user guides for your VMS. For practical examples in transport settings, review our people detection and vehicle detection resources: people detection in airports and vehicle detection and classification in airports.

