traditional video and ai video analytics
And, also, then, next, first, second, third, finally, however, therefore, thus, in addition, as well as, for example, for instance, besides. And, also, then, next, first, second, third, finally, however, therefore, thus, in addition, as well as, for example, for instance, besides.
Traditional video review depends on human eyes and manual playbacks. Security personnel watch recorded video, scrub timelines, and fast-forwarding through hours of footage to find critical moments. That manual video process is slow, repetitive, and error prone. By contrast, AI video analytics turns raw video into indexed data that operators can query. It automatically analyze video frames, extract metadata, and tag objects of interest. This change helps teams instantly find relevant video when seconds count and helps save valuable time during investigations.
Video surveillance historically meant one person per monitor and slow manual review. AI changes that by converting pixels into searchable metadata and structured records. The power of AI appears when the system can pinpoint specific people or vehicles and create searchable descriptions for recorded video. For example, a system that automatically tags a person wearing a red jacket lets an operator quickly search surveillance video for that person by clothing. The result is fast and accurate search results that reduce investigation time and improve operational efficiency.
Research shows surveillance videos contribute massively to unstructured big data, and object-based systems reshape how that video data is used (source). At the same time, converting video streams into digital objects raises legal questions because it “transforms raw video streams into digital objects,” a point made when discussing Fourth Amendment implications (source). Still, when sites use AI responsibly, operators can reduce false positives and improve response times.
AI models rely on object detection, classification, and tracking to build searchable indexes. Object detection extracts bounding boxes, and metadata captures attributes such as color, shape, and motion. These capabilities allow security teams to quickly search by attribute rather than by camera ID or date and time. For airports and perimeter sites, visionplatform.ai applies these techniques to existing cameras so installations do not need new camera infrastructure without replacing hardware. The platform turns traditional video into described events that operators and agents can act on.
For more on how specific detections work in practice, read about loitering and intrusion detection in airport settings where automated tagging helps investigators find specific incidents loitering detection and intrusion detection. These integrations illustrate how AI reduces investigation time and supports security personnel with richer context.
ai video search: search works in CCTV
And, also, then, next, first, second, third, finally, however, therefore, thus, in addition, as well as, for example, for instance, besides. And, also, then, next, first, second, third, finally, however, therefore, thus, in addition, as well as, for example, for instance, besides.
AI video search starts with object detection and ends with fast, relevant video retrieval. The pipeline begins when cameras stream frames into a detection engine. Object detection identifies people, vehicles, and other specific objects in each frame. The system then builds metadata records and indexes them by camera, timestamp, and attributes. After indexing, the search layer allows users to query the data in ways that feel like the way you search the web. VP Agent Search, for instance, converts streamed events and descriptions so operators can instantly find incidents from any location without knowing camera IDs.
Search works by matching query attributes to indexed metadata. You can search for people wearing a blue jacket, vehicles of a certain make, or objects that appear in a loading bay. Queries can include color, shape, direction of travel, and behavior. For example, an operator might request “red car at 3 pm” and receive pinpointed clips with a camera link and a short textual description. This approach yields fast and accurate search results and reduces hours of footage review to minutes.
The system supports queries across multiple cameras and across multiple cameras and sites. It also supports searches across all cameras so teams do not need to open each feed manually. That scalable approach lets security teams find specific events across large camera networks. Forensic search functions allow operators to view a specific date and then narrow to a specific date and time for detailed review. This is especially useful in busy environments like retail stores or transport hubs where many people or vehicles move through the space.
To illustrate, the search layer can automatically analyze video and return a video clip where a person loiters by a gate. VP Agent Search allows operators to search for people without remembering camera IDs. It allows users to search with natural language queries like “Person loitering near gate after hours” and then view a specific date and the camera by choosing to view a specific clip. For more on forensic search applied to airport scenarios see the forensic search page forensic search.

AI vision within minutes?
With our no-code platform you can just focus on your data, we’ll do the rest
smart video search for critical events
And, also, then, next, first, second, third, finally, however, therefore, thus, in addition, as well as, for example, for instance, besides. And, also, then, next, first, second, third, finally, however, therefore, thus, in addition, as well as, for example, for instance, besides.
Smart video search for critical events uses AI to identify not just objects but situations. It combines object detection with behavior analysis to spot intrusion, loitering, or other anomalies in real-time. That means the system can detect a person climbing a fence, a vehicle reversing in a pedestrian zone, or someone leaving an object behind. Smart video search tags these occurrences as critical events so operators get context, not just alarms. By design, it reduces the number of raw alerts and provides actionable intelligence that helps security teams act quickly.
Real-world cases show the impact. An intrusion alert can include a short video clip, metadata, and an explanation of what triggered the alarm. Loitering detection adds duration thresholds and behavioral context so operators see whether someone is indecisive or genuinely lingering. These features reduce false positives and help security personnel decide whether to dispatch officers, trigger gates, or escalate an incident. Studies suggest that active monitoring informed by analytics reduces crime more effectively and improves incident response times (study).
Smart video search also helps teams quickly pinpoint critical moments in long recordings. Instead of watching hours of footage, staff can find specific events and then scrub to the frame where the event began. That ability to find specific segments saves valuable time and shortens investigation time. For perimeter security and airports, this capability is essential. You can see how an airport application leverages behavioral detection in our loitering and people-detection materials people detection and loitering detection.
Smart video search amplifies the power of AI by providing both context and a workflow. Instead of sending out a simple alert, the system can summarize what happened, what was observed, and which objects of interest were involved. This delivers actionable insights to an operator and helps teams act quickly. The combination of detection accuracy and automated tagging yields a system that is both scalable and practical for busy control rooms.
ai-powered video analytics dashboard for security teams
And, also, then, next, first, second, third, finally, however, therefore, thus, in addition, as well as, for example, for instance, besides. And, also, then, next, first, second, third, finally, however, therefore, thus, in addition, as well as, for example, for instance, besides.
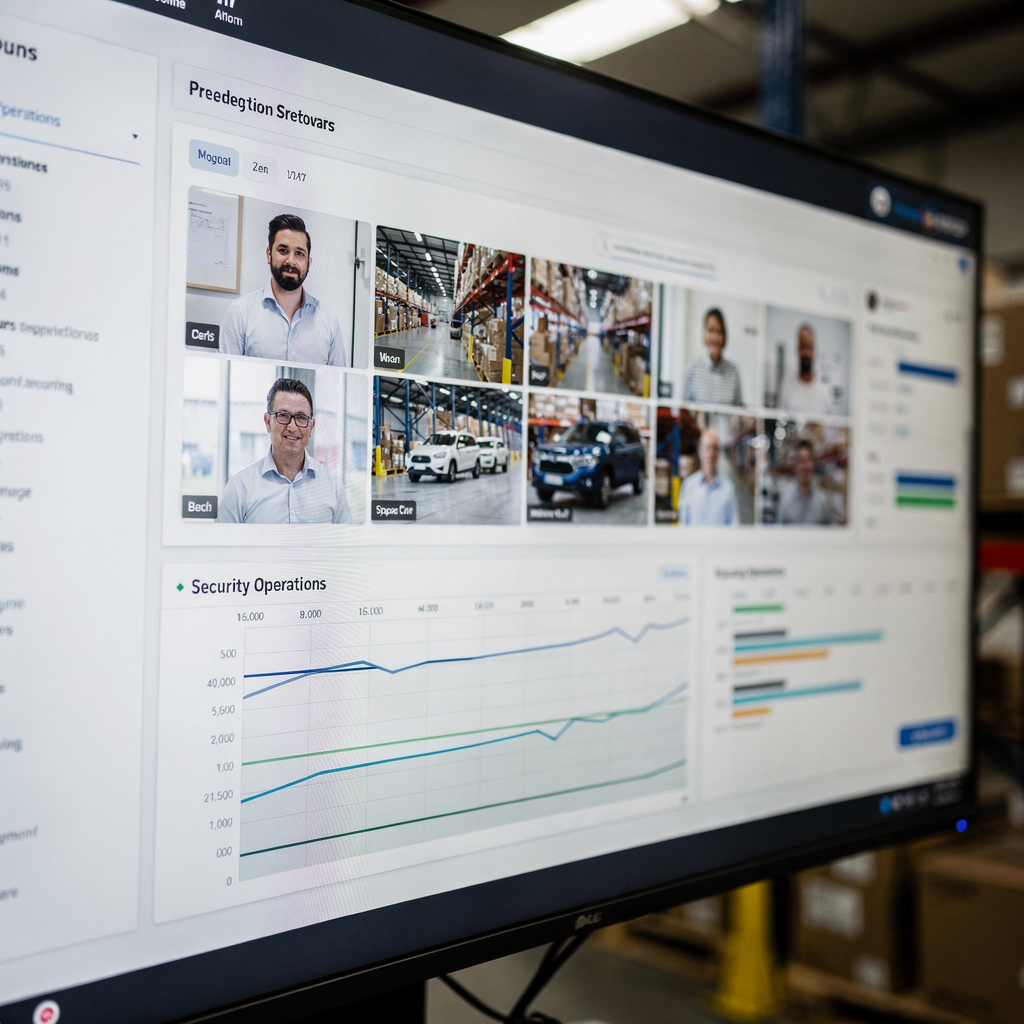
The dashboard is the operator’s command center. A modern dashboard aggregates detections, live feeds, and summaries. It shows counts of alerts, active incidents, and recent critical events. The interface supports drill-downs into metadata and lets users view a camera by choosing to view a specific clip. Operators can see the video management layer and open related logs or access control data for context. This single pane helps security teams coordinate and reduces the need to switch between separate tools.
AI-powered video analytics is built into the dashboard to surface the most important items first. Live tiles show real-time detection of people or vehicles and offer one-click playback for recorded video. The dashboard also displays heatmaps, object counts, and timelines so teams can quickly search for people or search for specific objects. When an alert appears, the panel shows the object, the confidence score, and the recommended next steps. That turns an alert into an explained situation.
Collaboration features matter. Security teams can annotate video clips, tag colleagues, and share incident packages. Reports can be exported with metadata and video clips for evidence. The VP Agent Suite, for example, not only feeds live alerts and summaries but also offers AI agents that suggest actions or pre-fill incident reports. This reduces manual tasks and helps teams focus on decisions instead of data gathering.
The dashboard also supports integrations with existing cameras and VMS platforms. It links to camera metadata and device health, and it can show incidents from any location across multiple cameras and sites. For organizations concerned about cloud processing, the platform supports on-prem deployments so metadata and models stay inside the site. This design choice helps meet compliance needs while keeping the dashboard responsive and operational.
AI vision within minutes?
With our no-code platform you can just focus on your data, we’ll do the rest
using ai to drive operational efficiency
And, also, then, next, first, second, third, finally, however, therefore, thus, in addition, as well as, for example, for instance, besides. And, also, then, next, first, second, third, finally, however, therefore, thus, in addition, as well as, for example, for instance, besides.
Using AI shifts the workload from manual to automated review. Instead of combing through hours of footage, analysts can focus on incidents flagged by AI. This reduces investigation time and decreases staff costs. For example, forensic search tools can cut a multi-hour review to minutes, so a single operator can process more incidents in a shift. These gains deliver measurable operational efficiency and let teams scale with demand.
AI systems also reduce the number of false alarms sent to security personnel. By correlating detections with context, an AI agent can verify whether an alarm is actionable. That means fewer unnecessary dispatches and lower alarm fatigue. The VP Agent Reasoning feature automates this by checking related systems, which helps avoid wasting resources. As a result, incident response times improve and operators can act with more confidence.
Scalable deployments matter when you manage thousands of cameras. A platform that can run on existing cameras and edge devices avoids a costly rip-and-replace of camera infrastructure without losing capability. It can automatically analyze video from many streams and scale across all cameras while preserving local control. This makes it practical to expand coverage, add analytics, and maintain consistent performance as networks grow.
Operational teams report reductions in time spent per case and in follow-up hours. Where manual video review once took days, AI search and tagging can find specific events and relevant footage in minutes. The power of AI here is not raw detection alone but the way it converts detections into readable summaries and recommended actions. For teams in busy environments such as airports and retail stores, this translates to faster investigations, fewer missed critical moments, and a more efficient use of personnel.
video search with natural language commands
And, also, then, next, first, second, third, finally, however, therefore, thus, in addition, as well as, for example, for instance, besides. And, also, then, next, first, second, third, finally, however, therefore, thus, in addition, as well as, for example, for instance, besides.
Natural language interfaces change how operators interact with video. Rather than building complex filters, an operator types or speaks a plain sentence. The system parses the sentence into object-level queries and returns matched clips. This mirrors the way you search the web and makes search capabilities accessible to non-technical staff. VP Agent Search enables forensic search using natural language, which helps teams instantly find specific incidents.
Natural language search allows operators to ask for a person by clothing, a vehicle by colour, or a behavior like loitering. The interface converts that request into an object-based query, then finds relevant video within the video footage. For example, an operator might ask to find a person wearing a blue jacket near gate B at a specific date and time. The system will search for people or vehicles and present matching recorded video and associated metadata.
Natural phrasing reduces training time and improves response under pressure. Instead of remembering camera names or timestamps, an operator can ask for incidents from any location and get guided results. This is particularly helpful when multiple teams need to coordinate quickly during an incident. Operators can annotate results, share them, and escalate based on the generated contextual summary.
Natural language search also supports advanced workflows. It allows users to view a specific date, scrub through the timeline, and choose the camera by choosing to view a clip directly from the query results. In addition, the system can automatically analyze video to produce short textual descriptions for each clip. With this approach, teams can find specific events rapidly, reduce incident response times, and improve the overall handling of potential threats.
FAQ
What is object-based video search for CCTV?
Object-based video search converts detected items in camera feeds into searchable objects. It enables operators to find relevant footage by querying attributes like colour, shape, or behavior.
How does AI improve traditional video review?
AI reduces manual video review by tagging and indexing events automatically. This saves valuable time and cuts down on hours of footage that staff must watch.
Can natural language queries really find events?
Yes. Natural language interfaces parse everyday phrases into object queries and return matching clips. This lets operators search without knowing camera IDs or timestamps.
Does AI work with existing cameras?
Many platforms run analytics on existing cameras and VMS systems, avoiding costly camera replacement. This preserves camera infrastructure without forcing a rip-and-replace.
How accurate are AI detections?
When optimised, AI video analytics can reach very high accuracy rates. For instance, some implementations report over 95% accuracy identifying people and vehicles in well-configured scenes (source).
Will this increase false alerts?
Properly tuned systems reduce false alerts by adding contextual verification. Systems that reason across data sources can lower nuisance alarms and provide actionable intelligence instead of raw alerts.
How does object-based search speed investigations?
Object-based search turns video data into metadata that can be queried quickly. Rather than scrubbing recorded video for hours, operators can instantly find relevant footage and quickly pinpoint critical events.
Is cloud processing required?
No. Some deployments offer on-prem, edge, or hybrid options so video and models remain local. That supports compliance needs and removes cloud dependency if sites prefer.
Can smart video search detect behaviors like loitering?
Yes. Smart video search combines object detection with behavior analysis to flag loitering, intrusions, and other critical events. For airport-specific examples, see the loitering and people detection resources loitering and people detection.
How do dashboards help security teams?
Dashboards aggregate live alerts, summaries, and tools for collaboration. They let teams annotate clips, share incidents, and act quickly based on AI-powered summaries that turn detections into decisions.

